| NNNN BAD DEVELOPERS NNNN | |||||||||||||
|
EXPOSING DEVELOPERS WHO FAIL TO APPRECIATE AND RESPECT COMMUNITY, ENVIRONMENT AND SPIRIT OF THE LAND |
|||||||||||||
Reservoirs poisoned with Atrazine 1997-8 (Comprehensive Background information about this issue)
According to the SA EPA "In 1998 Atrazine, Hexazinone and Simazine were detected in Barossa, Millbrook, Mount Bold, Myponga, Happy Valley, Warren and South Para Reservoirs"
Map of SA plantations in domestic water supplies can be found here.

The riskiest plantations in Australia? - In terms of impacts to water quality.
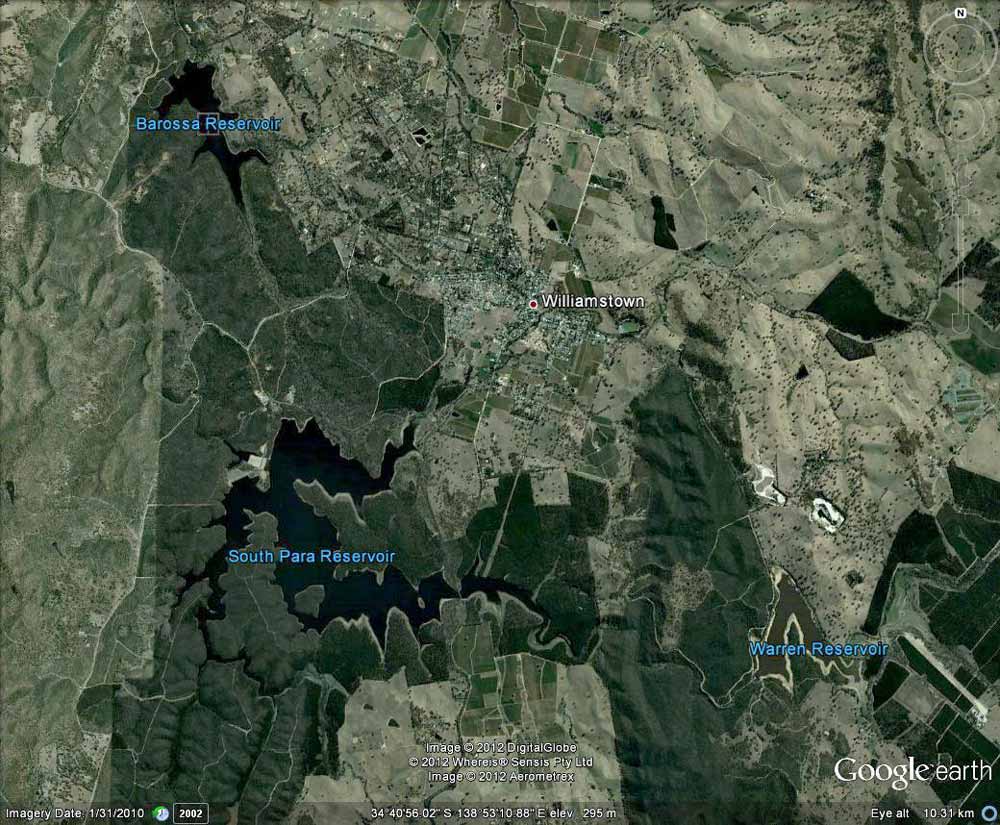
Barossa Reservoir supplies drinking water to Gawler (Munno Para and Elizabeth). Water comes from South Para Reservoir and South Para River Ė supplemented from Warren Reservoir and Murray River. South Para Reservoir supplied by Mannum-Adelaide Pipeline.
Other communities supplied through Barossa Water Treatment Plant Supply Area: Elizabeth Park, Elizabeth East, Waterloo Corner, Burton, Munno Para, Smithfield, Evanston Gardens, Gawler River, Gawler, Two Wells, Williamstown, Cockatoo Valley, Roseworthy, Wasleys, Redbanks, Mallala, Dublin, Windsor, Port Parham, Hamley Bridge, Owen
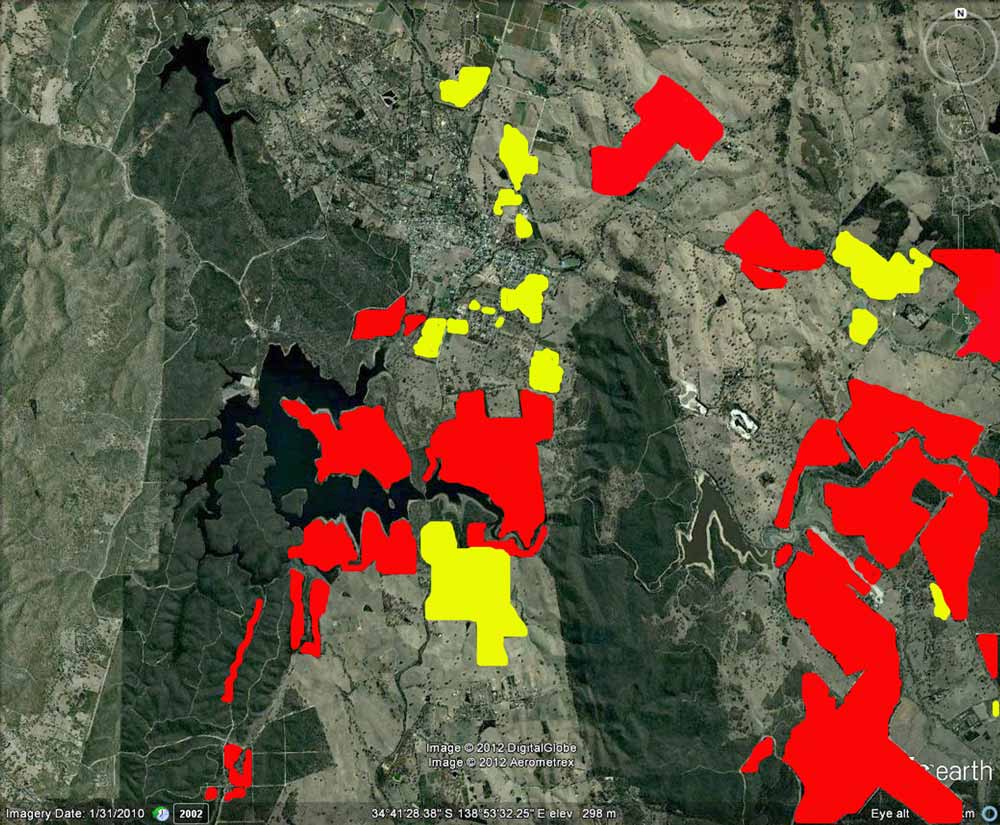
Red = plantations, yellow = vineyards
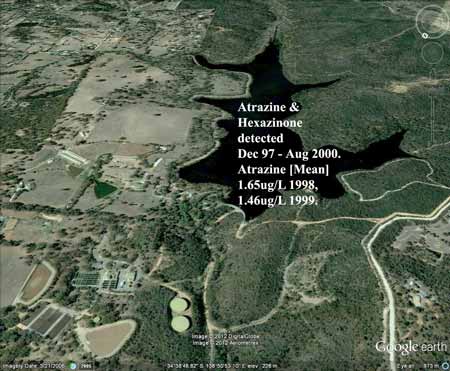
"... ATRAZINE ENTERING WATER FROM FORESTRY ACTIVITIES The Environment Protection Authority has recently been advised by the SA Water Corporation that the herbicide atrazine has been detected in the Barossa Reservoir continuously since September 1997 and that normal water filtration processes have not been able to remove atrazine from the water supply system. It is also understood that investigations conducted by SA Water since June 1998 have indicated that: water in South Para and Warren Reservoirs contains atrazine at similar concentrations to that found in the Barossa Reservoir...In accordance with the objects of the Environment Protection Act 1993, which provide for application of the precautionary principle, and the general environmental duty contained in Section 25 of the Act, the Authority directs Forestry SA to cease the use of Atrazine and other herbicides in all of the proclaimed water protection areas within the Mt Lofty Ranges until such time as a management plan is developed by Forestry SA to the satisfaction of the Authority which seeks to avoid herbicides entering water bodies from forestry areas..." Letter from Executive Director EPA to General Manager Forestry SA 3 August 1998
"... Atrazine was detected by SA Water at Barossa Reservoir last September [1997], but it was only made public through a press release issued after 11pm on Tuesday [15 Sep 1998]. The notification followed an EPA investigation which found the contamination had travelled down creek beds from the SA Forestry plantation to the Warren, South Para and Barossa Reservoirs..." The Advertiser Sep 17 1998
"In order to guarantee the safety of the water supply, SA Water has initaited powdered activated carbon treatment of the water produced by United Water at Barossa Water Treatment Plant. It is expected that this treatment will enable levels in the Barossa distribution system to be maintained below analytical limits. This will be verified by WTP product water analyses..." SA Water Briefing Note 55/98 16 July 1998.
"... Samples from streams draining through the plantation areas (which then drain into Warren Reservoir) show herbicide levels around 150ug/L, which are up to six times the level recommended for drinking water. These levels are also significant from an environmental viewpoint and the EPA is likely to take an active interest. Dosing of powder activated carbon has been instigated at Barossa Water Treatment Plant in order to prevent the herbicides passing into supply. At present, herbicide concentrations in the treated water leaving Barossa plant are below the limit of detection (currently 1.2ug/L) against the guideline (0.5ug/L) and health limits (20ug/L) set within the Australian Drinking Water Guidelines. Provided the herbicide concentrations in the raw water entering the Barossa treatment plant remain below around 2-3ug/L, existing powder activated carbon dosing at the plant is expected to remain effective in controlling herbicide levels in treated water. Dosing costs are currently $30,000 per month. Should herbicide concentrations increase significantly then further temporary dosing facilities will need to be installed at the plant and dosing costs will also increase significantly..." SA Water Briefing Paper - No. 69/98 29 July 1998.
"SA Water continues to dose powder activated carbon (20mg/L) into the raw water entering Barossa WTP in order to ansure that no herbicides reach customers. Product water analyses have demonstrated effective removal..." SA Water Briefing Paper - No. 113 10 September 1998
"Atrazine was regularly dropped by helicopter near most of the state reservoirs to control weeds in new forestry plantations. In late 1997, large quantities leached into Warren Reservoir after heavy rain dissolved clay pellets coated with the chemical..." The Advertiser Jan 24 2001
"Forestry SA has stopped using a herbicide linked overseas to cancer, says Government Minister Michael Armitage. The department ceased treating new pine plantations with Atrazine in May 1998...Since the early 1970's, Forestry SA has used to bomb new pine plantations around reservoirs with herbicides containing atrazine... SA Water spent an estimated $700,000 in 1998 treating contaminated water with an expensive chemical before it was released for drinking water supplies. The corporation wanted to sue Forestry SA to recover the cost ..." The Advertiser January 10 2001
A State Government department was ordered to stop using potentially carconogenic herbicides after its operations contaminated drinking water supplies. The Environment Protection Authority issued the edict to Forestry SA in August 1998 after herbicides were traced to new pine plantations near the Barossa Valley..." The Advertiser January 24 2001
Barossa Reservoir poisoned with forestry herbicides Atrazine and Hexazinone 1997-2000. (Please note that detections were initially recorded at Barossa Reservoir from September 1997. The following data is sourced from after this date by almost a year, except for Barossa Reservoir Location 1, where detections are included from December 1997, 3 months after initial incident).
Details
Barossa Reservoir Location 1
Atrazine: 2.1ug/L (11 Dec 97), 2ug/L (22/1/98), 2ug/L (19/2/98), 2ug/L (19/3/98), 2.38ug/L (16/4/98), 2.1ug/L (14/5/98), 1.54ug/L (11/6/98), 1.63ug/L (9/7/98), 1.92ug/L (23/7/98), 1.96ug/L (30/7/98), 1.69ug/L (3 Aug 98), 1.63ug/L (6 Aug 98), 1.7ug/L (20 Aug 98), 1.87ug/L (3 Sep 98), 1.75ug/L (17 Sep 98), 1.25ug/L (1 Oct 98), 1.46ug/L (15 Oct 98), 1.33ug/L (29 Oct 98), 1.4ug/L (4 Nov 98), 1.34ug/L (11 Nov 98), 1.58ug/L (18 Nov 98), 1.39ug/L (25 Nov 98), 1.24ug/L (2 Dec 98), 1.5ug/L (9 Dec 98), 1.57ug/L (16 Dec 98), 1.38ug/L (23 Dec 98), 1.33ug/L (30 Dec 98), 1.6ug/L (6 Jan 99), 1.49ug/L (13 Jan 99), 1.46ug/L (20 Jan 99), 1.29ug/L (27 Jan 99), 1.38ug/L (3 Feb 99), 1.53ug/L (10 Feb 99), 1.47ug/L (17 Feb 99), 1.8ug/L (24 Feb 99), 1.6ug/L (3 Mar 99), 1.5ug/L (10 Mar 99), 1.8ug/L (17 Mar 99), 1.8ug/L (24 Mar 99), 1.8ug/L (31 Mar 99), 1.7ug/L (7 Apr 99), 1.6ug/L (15 Apr 99), 1.6ug/L (22 Apr 99), 1.6ug/L (12 May 99), 1.6ug/L (19 May 99), 1.4ug/L (25 May 99), 1.4ug/L (2 Jun 99), 1.3ug/L (9 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (16 Jun 99), 1.5ug/L (23 Jun 99), 1.5ug/L (30 Jun 99), 1.5ug/L (7 Jul 99), 1.5ug/L (14 Jul 99), 2.2ug/L (21 Jul 99), 1.3ug/L (28 Jul 99), 1.5ug/L (4 Aug 99), 1.3ug/L (11 Aug 99), 1ug/L (18 Aug 99), 1.2ug/L (25 Aug 99), 1.1ug/L (1 Sep 99), 1.6ug/L (8 Sep 99), 1.1ug/L (15 Sep 99), 1ug/L (13 Oct 99), 1.1ug/L (11 Nov 99), 0.9ug/L (16 Dec 99), 0.8ug/L (13 Jan 00), 0.9ug/L (17 Feb 00), 0.9ug/L (16 Mar 00), 0.7ug/L (13 Apr 00), 0.7ug/L (11 May 00), 0.6ug/L (15 Jun 00), 0.6ug/L (13 Jul 00), 0.5ug/L (17 Aug 00),
Hexazinone: 1.5ug/L (11 Dec 97), 1.55ug/L (16 Apr 98), 1.67ug/L (3 Sep 98), 1.46ug/L (17 Sep 98), 1.12ug/L (1 Oct 98), 1.59ug/L (15 Oct 98), 1.43ug/L (29 Oct 98), 1.55ug/L (4 Nov 98), 1.96ug/L (11 Nov 98), 1.73ug/L (18 Nov 98), 1.15ug/L (25 Nov 98), 1.41ug/L (2 Dec 98), 1.25ug/L (9 Dec 98), 1.37ug/L (16 Dec 98), 1.43ug/L (23 Dec 98), 1.35ug/L (30 Dec 98), 1.43ug/L (6 Jan 99), 1.24ug/L (13 Jan 99), 1.45ug/L (20 Jan 99), 1.2ug/L (27 Jan 99), 1.44ug/L (3 Feb 99), 1.61ug/L (10 Feb 99), 1.62ug/L (17 Feb 99), 1.6ug/L (24 Feb 99), 1.7ug/L (3 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (10 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (17 Mar 99), 1.5ug/L (24 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (31 Mar 99), 1.5ug/L (7 Apr 99), 1.4ug/L (15 Apr 99), 1.4ug/L (22 Apr 99), 1.5ug/L (12 May 99), 1.3ug/L (19 May 99), 1.9ug/L (25 May 99), 1.4ug/L (2 Jun 99), 1.3ug/L (9 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (16 Jun 99), 1.6ug/L (23 Jun 99), 1.3ug/L (30 Jun 99), 1.5ug/L (7 Jul 99), 1.4ug/L (14 Jul 99), 1.5ug/L (21 Jul 99), 1.4ug/L (28 Jul 99), 1.4ug/L (4 Aug 99), 1.3ug/L (11 Aug 99), 1.5ug/L (18 Aug 99), 1.3ug/L (25 Aug 99), 1.3ug/L (1 Sep 99), 1.4ug/L (8 Sep 99), 1.6ug/L (15 Sep 99), 1.1ug/L (13 Oct 99), 1.2ug/L (11 Nov 99), 0.9ug/L (16 Dec 99), 1ug/L (13 Jan 00), 1ug/L (17 Feb 00), 1ug/L (16 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (13 Apr 00), 0.7ug/L (11 May 00), 0.8ug/L (15 Jun 00), 0.9ug/L (13 Jul 00), 0.8ug/L (17 Aug 00), 0.7ug/L (21 Sep 00).
Simazine: 0.5ug/L (23 Jun 99).
Barossa Weir
Atrazine: 1.47ug/L (9/7/98), 1.81ug/L (23/7/98), 1.73ug/L (6 Aug 98), 1.48ug/L (25 Sep 98), 1.46ug/L (15 Oct 98), 1.5ug/L (3 Dec 98), 1.69ug/L (17 Dec 98), 1.61ug/L (7 Jan 99), 1.58ug/L (14 Jan 99), 1.49ug/L (21 Jan 99), 1.52ug/L (28 Jan 99), 1.55ug/L (4 Feb 99), 1.8ug/L (18 Mar 99), 1.9ug/L (22 Mar 99), 1.5ug/L (13 May 99), 1.6ug/L (25 May 99), 1.4ug/L (29 May 99), 1.3ug/L (7 Jun 99), 1.3ug/L (13 Jun 99), 1.2ug/L (18 Jun 99), 1.2ug/L (9 Jul 99), 1.1ug/L (19 Jul 99), 1.1ug/L (9 Aug 99), 1.6ug/L (4 Sep 99), 1ug/L (29 Sep 99), 0.9ug/L (3 Oct 99), 0.9ug/L (10 Oct 99), 0.8ug/L (13 Oct 99), 0.8ug/L (10 Nov 99), 0.8ug/L (22 Nov 99), 0.8ug/L (3 Dec 99), 0.8ug/L (21 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (24 Feb 00), 0.7ug/L (9 Mar 00), 0.7ug/L (23 Mar 00), 0.7ug/L (14 Apr 00), 0.6ug/L (20 Apr 00), 0.6ug/L (30 Apr 00), 0.6ug/L (13 May 00), 0.6ug/L (18 May 00), 0.5ug/L (27 May 00), 0.6ug/L (6 Jun 00), 0.5ug/L (22 Jun 00), 0.5ug/L (28 Jun 00).
Hexazinone: 1.27ug/L (25 Sep 98), 1.49ug/L (15 Oct 98), 1.63ug/L (3 Dec 98), 1.59ug/L (17 Dec 98), 1.51ug/L (7 Jan 99), 1.34ug/L (14 Jan 99), 1.31ug/L (21 Jan 99), 1.34ug/L (28 Jan 99), 1.36ug/L (4 Feb 99), 1.5ug/L (18 Mar 99), 1.5ug/L (22 Mar 99), 1.1ug/L (13 May 99), 1.4ug/L (25 May 99), 1.4ug/L (29 May 99), 1.2ug/L (7 Jun 99), 1.3ug/L (13 Jun 99), 1.2ug/L (18 Jun 99), 1.3ug/L (9 Jul 99), 1.2ug/L (19 Jul 99), 1.3ug/L (4 Sep 99), 0.9ug/L (29 Sep 99), 1ug/L (3 Oct 99), 1ug/L (10 Oct 99), 0.8ug/L (13 Oct 99), 1ug/L (10 Nov 99), 1ug/L (22 Nov 99), 0.9ug/L (3 Dec 99), 0.7ug/L (21 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (24 Feb 00), 0.9ug/L (9 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (23 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (14 Apr 00), 0.8ug/L (20 Apr 00), 0.7ug/L (30 Apr 00), 0.8ug/L (13 May 00), 0.7ug/L (18 May 00), 0.6ug/L (23 May 00), 0.7ug/L (22 Jun 00), 0.8ug/L (28 Jun 00), 0.7ug/L (20 Jul 00), 0.7ug/L (26 Jul 00), 0.5ug/L (23 Aug 00).
Simazine: 0.6ug/L (23 Jun 04)
Barossa Water Treatment Plant Inlet
Atrazine: 3.41ug/L (3 Aug 98), 1.7ug/L (10 Aug 98), 1.61ug/L (24 Aug 98), 1.48ug/L (14 Sep 98), 1.73ug/L (16 Sep 98), 1.85ug/L (21 Sep 98), 1.38ug/L (28 Sep 98), 1.19ug/L (7 Oct 98), 1.03ug/L (12 Oct 98), 1.48ug/L (19 Oct 98), 1.48ug/L (26 Oct 98), 1.34ug/L (4 Nov 98), 1.26ug/L (5 Nov 98), 1.29ug/L (11 Nov 98), 1.28ug/L (16 Nov 98), 1.47ug/L (17 Nov 98), 1.41ug/L (24 Nov 98), 1.36ug/L (1 Dec 98), 1.53ug/L (7 Dec 98), 1.66ug/L (14 Dec 98), 1.37ug/L (23 Dec 98), 1.3ug/L (28 Dec 98), 1.52ug/L (1 Jan 99), 1.61ug/L (4 Jan 99), 1.59ug/L (11 Jan 99), 1.42ug/L (15 Jan 99), 1.41ug/L (20 Jan 99), 1.42ug/L (25 Jan 99), 1.41ug/L (1 Feb 99), 1.8ug/L (22 Feb 99), 2.3ug/L (1 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (8 Mar 99), 1.8ug/L (15 Mar 99), 1.8ug/L (22 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (29 Mar 99), 1.7ug/L (5 Apr 99), 1.6ug/L (12 Apr 99), 1.6ug/L (19 Apr 99), 1.6ug/L (26 Apr 99), 1.6ug/L (3 May 99), 1.4ug/L (18 May 99), 1.6ug/L (19 May 99), 1.3ug/L (31 May 99), 0.9ug/L (7 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (15 Jun 99), 1.5ug/L (21 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (28 Jun 99), 1.5ug/L (5 Jul 99), 1.5ug/L (7 Jul 99), 1.5ug/L (19 Jul 99), 1.5ug/L (22 Jul 99), 1.3ug/L (27 Jul 99), 1.4ug/L (2 Aug 99), 1.3ug/L (16 Aug 99), 1.5ug/L (19 Aug 99), 1.4ug/L (23 Aug 99), 1.3ug/L (30 Aug 99), 1.7ug/L (6 Sep 99), 1.2ug/L (13 Sep 99), 1.3ug/L (17 Sep 99), 1.4ug/L (20 Sep 99), 1ug/L (27 Sep 99), 1.1ug/L (5 Oct 99), 1.1ug/L (11 Oct 99), 0.8ug/L (18 Oct 99), 0.9ug/L (25 Oct 99), 1ug/L (1 Nov 99), 1.2ug/L (8 Nov 99), 1.2ug/L (15 Nov 99), 1.1ug/L (22 Nov 99), 1ug/L (29 Nov 99), 1ug/L (6 Dec 99), 1.1ug/L (13 Dec 99), 1ug/L (20 Dec 99), 1ug/L (27 Dec 99), 1.1ug/L (10 Jan 00), 0.8ug/L (17 Jan 00), 0.9ug/L (24 Jan 00), 0.8ug/L (31 Jan 00), 1ug/L (7 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (14 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (21 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (28 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (6 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (13 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (20 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (27 Mar 00), 0.7ug/L (3 Apr 00), 0.6ug/L (10 Apr 00), 0.7ug/L (17 Apr 00), 0.8ug/L (26 Apr 00), 0.7ug/L (1 May 00), 0.8ug/L (8 May 00), 0.8ug/L (15 May 00), 0.8ug/L (5 Jun 00), 0.8ug/L (12 Jun 00), 0.6ug/L (19 Jun 00), 0.5ug/L (25 Jun 00), 0.6ug/L (3 Jul 00), 0.6ug/L (10 Jul 00), 0.6ug/L (17 Jul 00), 0.5ug/L (24 Jul 00), 0.5ug/L (31 Jul 00), 0.5ug/L (7 Aug 00), 0.5ug/L (14 Aug 00), 0.5ug/L (28 Aug 00), 0.5ug/L (18 Sep 00), 0.6ug/L (25 Sep 00).
Hexazinone: 1.34ug/L (14 Sep 98), 1.46ug/L (16 Sep 98), 1.49ug/L (21 Sep 98), 1.08ug/L (28 Sep 98), 1.21ug/L (7 Oct 98), 1.23ug/L (12 Sep 98), 1.36ug/L (19 Oct 98), 1.53ug/L (26 Oct 98), 1.42ug/L (4 Nov 98), 1.28ug/L (5 Nov 98), 1.8ug/L (11 Nov 98), 1.34ug/L (16 Nov 98), 0.93ug/L (17 Nov 98), 1.01ug/L (24 Nov 98), 2.07ug/L (1 Dec 98), 1.35ug/L (7 Dec 98), 1.3ug/L (14 Dec 98), 1.29ug/L (23 Dec 98), 1.34ug/L (28 Dec 98), 1.46ug/L (1 Jan 99), 1.49ug/L (4 Jan 99), 1.31ug/L (11 Jan 99), 1.33ug/L (15 Jan 99), 1.33ug/L (20 Jan 99), 1.24ug/L (25 Jan 99), 1.31ug/L (1 Feb 99), 1.5ug/L (22 Feb 99), 1.4ug/L (1 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (8 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (15 Mar 99), 1.3ug/L (22 Mar 99), 1.5ug/L (29 Mar 99), 1.4ug/L (5 Apr 99), 1.5ug/L (12 Apr 99), 1.4ug/L (19 Apr 99), 1.4ug/L (26 Apr 99), 1.4ug/L (3 May 99), 1.5ug/L (10 May 99), 1.4ug/L (18 May 99), 1.2ug/L (19 May 99), 1.2ug/L (31 May 99), 1.1ug/L (7 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (15 Jun 99), 1.6ug/L (21 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (28 Jun 99), 1.3ug/L (5 Jul 99), 1.5ug/L (7 Jul 99), 1.6ug/L (19 Jul 99), 1.6ug/L (22 Jul 99), 1.7ug/L (27 Jul 99), 1.4ug/L (2 Aug 99), 1.2ug/L (16 Aug 99), 1.5ug/L (19 Aug 99), 1.4ug/L (23 Aug 99), 1.4ug/L (30 Aug 99), 1.3ug/L (6 Sep 99), 1.4ug/L (13 Sep 99), 1.6ug/L (17 Sep 99), 1.4ug/L (20 Sep 99), 1.2ug/L (27 Sep 99), 1.2ug/L (5 Oct 99), 1.6ug/L (11 Oct 99), 0.9ug/L (18 Oct 99), 1ug/L (25 Oct 99), 1.2ug/L (1 Nov 99), 1ug/L (8 Nov 99), 1.3ug/L (15 Nov 99), 1.3ug/L (22 Nov 99), 1.1ug/L (29 Nov 99), 0.9ug/L (6 Dec 99), 0.9ug/L (13 Nov 99), 1ug/L (20 Dec 99), 1ug/L (27 Dec 99), 1.2ug/L (10 Jan 00), 0.8ug/L (17 Jan 00), 1.2ug/L (24 Jan 00), 1ug/L (31 Jan 00), 1ug/L (7 Feb 00), 0.9ug/L (14 Feb 00), 0.9ug/L (21 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (28 Feb 00), 0.9ug/L (6 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (13 Mar 00), 0.9ug/L (20 Mar 00), 0.9ug/L (27 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (3 Apr 00), 0.8ug/L (10 Apr 00), 0.8ug/L (17 Apr 00), 0.8ug/L (26 Apr 00), 0.8ug/L (1 May 00), 0.8ug/L (8 May 00), 0.8ug/L (15 May 00), 0.6ug/L (29 May 00), 0.8ug/L (5 Jun 00), 0.7ug/L (12 Jun 00), 0.8ug/L (19 Jun 00), 0.8ug/L (25 Jun 00), 0.9ug/L (3 Jul 00), 0.9ug/L (10 Jul 00), 1ug/L (17 Jul 00), 0.8ug/L (24 Jul 00), 0.8ug/L (31 Jul 00), 0.8ug/L (7 Aug 00), 0.7ug/L (14 Aug 00), 0.7ug/L (21 Aug 00), 0.7ug/L (28 Aug 00), 0.8ug/L (4 Sep 00), 0.6ug/L (11 Sep 00), 0.7ug/L (18 Sep 00), 0.6ug/L (25 Sep 00), 0.6ug/L (2 Oct 00), 0.5ug/L (9 Oct 00), 0.5ug/L (22 Oct 00), 0.6ug/L (23 Oct 00), 0.5ug/L (6 Nov 00), 0.5ug/L (13 Nov 00).
Diazinon: 0.6ug/L (24 Aug 98)
Barossa Water Treatment Plant Before Storage
Atrazine: 1.9ug/L (16 Jun 98), 1.75ug/L (29 Jun 98), 2.33ug/L (10 Jul 98), 0.69ug/L (7 Sep 98), 0.68ug/L (16 Sep 98), 1.19ug/L (19 Oct 98), 1.38ug/L (26 Oct 98), 1.22ug/L (4 Nov 98), 0.62ug/L (5 Nov 98), 1.29ug/L (16 Nov 98), 0.5ug/L (15 Mar 99), 0.8ug/L (19 Jul 99), 0.8ug/L (21 Jul 99), 0.8ug/L (22 Jul 99), 0.5ug/L (27 Jul 99), 0.7ug/L (2 Aug 99), 1.2ug/L (6 Sep 99), 1ug/L (13 Sep 99), 1ug/L (20 Sep 99), 1ug/L (27 Sep 99), 1.2ug/L (5 Oct 99), 1ug/L (11 Oct 99), 0.9ug/L (18 Oct 99), 0.8ug/L (25 Oct 99), 0.9ug/L (1 Nov 99), 1.1ug/L (8 Nov 99), 1ug/L (15 Nov 99), 1.1ug/L (22 Nov 99), 0.9ug/L (29 Nov 99), 0.9ug/L (6 Dec 99), 0.8ug/L (13 Dec 99), 1ug/L (20 Dec 99), 0.9ug/L (27 Dec 99), 1ug/L (4 Jan 00), 1ug/L (10 Jan 00), 0.8ug/L (17 Jan 00), 0.9ug/L (24 Jan 00), 0.9ug/L (31 Jan 00), 0.8ug/L (7 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (14 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (21 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (28 Feb 00), 0.7ug/L (6 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (13 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (20 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (27 Mar 00), 0.7ug/L (3 Apr 00), 0.6ug/L (10 Apr 00), 0.7ug/L (17 Apr 00), 0.8ug/L (26 Apr 00), 0.7ug/L (1 May 00), 0.8ug/L (8 May 00), 0.8ug/L (15 May 00), 0.8ug/L (5 Jun 00), 0.8ug/L (12 Jun 00), 0.6ug/L (19 Jun 00), 0.5ug/L (25 Jun 00), 0.6ug/L (3 Jul 00), 0.6ug/L (10 Jul 00), 0.6ug/L (17 Jul 00), 0.5ug/L (7 Aug 00).
Hexazinone: 4.16ug/L (10 Jul 98), 0.98ug/L (7 Sep 98), 0.97ug/L (16 Sep 98), 0.63ug/L (21 Sep 98), 1.29ug/L (19 Oct 98), 1.23ug/L (26 Oct 98), 1.45ug/L (4 Nov 98), 0.92ug/L (5 Nov 98), 0.74ug/L (11 Nov 98), 1.29ug/L (16 Nov 98), 0.77ug/L (1 Dec 98), 0.75ug/L (7 Dec 98), 1.44ug/L (9 Dec 98), 1.86ug/L (16 Dec 98), 1.44ug/L (23 Dec 98), 1.52ug/L (6 Jan 99), 0.5ug/L (27 Jan 99), 0.55ug/L (15 Feb 99), 0.6ug/L (22 Feb 99), 0.7ug/L (8 Mar 99), 0.6ug/L (15 Mar 99), 0.6ug/L (20 Mar 99), 0.6ug/L (22 Mar 99), 0.7ug/L (29 Mar 99), 0.6ug/L (5 Apr 99), 0.6ug/L (12 Apr 99), 0.5ug/L (26 Apr 99), 0.6ug/L (3 May 99), 1.1ug/L (10 May 99), 0.8ug/L (24 May 99), 0.8ug/L (7 Jun 99), 0.6ug/L (15 Jun 99), 0.6ug/L (21 Jun 99), 0.8ug/L (28 Jun 99), 0.5ug/L (5 Jul 99), 0.5ug/L (7 Jul 99), 1ug/L (19 Jul 99), 1.4ug/L (21 Jul 99), 1.1ug/L (22 Jul 99), 0.8ug/L (27 Jul 99), 1ug/L (2 Aug 99), 0.5ug/L (16 Aug 99), 0.5ug/L (19 Aug 99), 1.2ug/L (6 Sep 99), 1.3ug/L (13 Sep 99), 1.2ug/L (20 Sep 99), 1.3ug/L (27 Sep 99), 1ug/L (5 Oct 99), 1.2ug/L (11 Oct 99), 0.9ug/L (18 Oct 99), 0.9ug/L (25 Oct 99), 1.1ug/L (1 Nov 99), 1ug/L (8 Nov 99), 1.1ug/L (15 Nov 99), 1ug/L (22 Nov 99), 1ug/L (29 Nov 99), 0.9ug/L (6 Dec 99), 0.8ug/L (13 Dec 99), 1ug/L (20 Dec 99), 0.9ug/L (27 Dec 99), 0.9ug/L (4 Jan 00), 1.1ug/L (10 Jan 00), 0.8ug/L (17 Jan 00), 1ug/L (24 Jan 00), 1ug/L (31 Jan 00), 0.9ug/L (7 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (14 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (21 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (28 Feb 00), 0.8ug/L (6 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (13 Mar 00), 0.9ug/L (20 Mar 00), 0.8ug/L (27 Mar 00), 0.7ug/L (3 Apr 00), 0.8ug/L (10 Apr 00), 0.7ug/L (17 Apr 00), 0.7ug/L (26 Apr 00), 0.8ug/L (8 May 00), 0.7ug/L (15 May 00), 0.7ug/L (23 May 00), 0.6ug/L (29 May 00), 0.8ug/L (5 Jun 00), 0.8ug/L (19 Jun 00), 0.7ug/L (25 Jun 00), 0.8ug/L (3 Jul 00), 0.9ug/L (10 Jul 00), 0.8ug/L (17 Jul 00), 0.8ug/L (24 Jul 00), 0.8ug/L (31 Jul 00), 0.8ug/L (7 Aug 00), 0.6ug/L (14 Aug 00), 0.6ug/L (21 Aug 00), 0.6ug/L (28 Aug 00), 0.7ug/L (4 Sep 00), 0.6ug/L (11 Sep 00), 0.6ug/L (18 Sep 00), 0.5ug/L (25 Sep 00), 0.5ug/L (2 Oct 00), 0.5ug/L (9 Oct 00), 0.5ug/L (23 Oct 00), 0.5ug/L (30 Oct 00), 0.6ug/L (13 Nov 00),
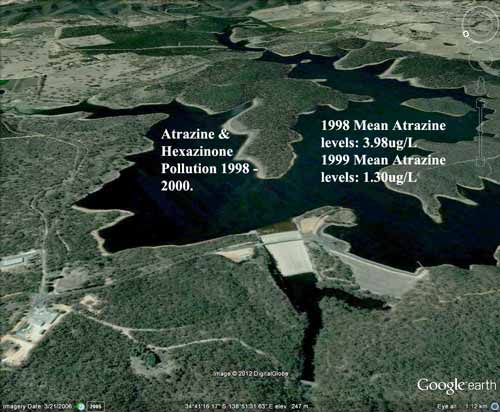
South Para Reservoir poisoned with forestry herbicides Atrazine and Hexazinone 1998-2000.
South Para Reservoir Location 1
Atrazine: 2.26ug/L (18 Jun 98), 1.74ug/L (16 Jul 98), 1.99ug/L (30 Jul 98), 43.6ug/L (30 Jul 98), 3.64ug/L (30 Jul 98), 4.91ug/L (30 Jul 98), 4.52ug/L (30 Jul 98), 1.85ug/L (30 Jul 98), 4.85ug/L (3 Aug 98), 1.85ug/L (3 Aug 98), 1.95ug/L (13 Aug 98), 2.12ug/L (27 Aug 98), 1.85ug/L (10 Sep 98), 1.77ug/L (24 Sep 98), 1.4ug/L (8 Oct 98), 1.57ug/L (29 Oct 98), 1.75ug/L (4 Nov 98), 1.56ug/L (11 Nov 98), 1.98ug/L (18 Nov 98), 1.98ug/L (25 Nov 98), 1.33ug/L (2 Dec 98), 1.57ug/L (9 Dec 98), 1.66ug/L (16 Dec 98), 1.88ug/L (23 Dec 98), 1.6ug/L (6 Jan 99), 1.49ug/L (13 Jan 99), 1.45ug/L (20 Jan 99), 1.49ug/L (27 Jan 99), 1.39ug/L (3 Feb 99), 1.5ug/L (10 Feb 99), 1.6ug/L (17 Feb 99), 1.8ug/L (24 Feb 99), 1.6ug/L (3 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (10 Mar 99), 1.8ug/L (17 Mar 99), 1.8ug/L (24 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (31 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (7 Apr 99), 1.5ug/L (15 Apr 99), 1.6ug/L (22 Apr 99), 1.5ug/L (28 Apr 99), 1.3ug/L (12 May 99), 1.4ug/L (19 May 99), 1.3ug/L (26 May 99), 1.4ug/L (2 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (9 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (16 Jun 99), 1.2ug/L (23 Jun 99), 1.2ug/L (30 Jun 99), 1.2ug/L (7 Jul 99), 1.1ug/L (14 Jul 99), 1.1ug/L (21 Jul 99), 1ug/L (28 Jul 99), 1.3ug/L (4 Aug 99), 1.3ug/L (11 Aug 99), 1ug/L (18 Aug 99), 0.9ug/L (25 Aug 99), 1.2ug/L (1 Sep 99), 1.2ug/L (8 Sep 99), 0.7ug/L (15 Sep 99), 0.7ug/L (13 Oct 99), 0.8ug/L (11 Nov 99), 0.7ug/L (16 Dec 99), 0.8ug/L (13 Jan 00), 0.8ug/L (17 Feb 00), 0.9ug/L (16 Mar 00), 0.6ug/L (13 Apr 00), 0.6ug/L (11 May 00), 0.5ug/L (15 Jun 00).
Hexazinone: 35.4ug/L (30/7/98), 3ug/L (30 Jul 98), 5.33ug/L (30 Jul 98), 4.89ug/L (30 Jul 98), 5.12ug/L (3 Aug 98), 1.8ug/L (27 Aug 98), 1.71ug/L (10 Sep 98), 1.68ug/L (24 Sep 98), 1.55ug/L (8 Oct 98), 1.62ug/L (29 Oct 98), 2.16ug/L (4 Nov 98), 2.03ug/L (11 Nov 98), 1.7ug/L (18 Nov 98), 1.17ug/L (25 Nov 98), 1.41ug/L (2 Dec 98), 4.44ug/L (9 Dec 98), 4.13ug/L (16 Dec 98), 3.83ug/L (23 Dec 98), 1.24ug/L (13 Jan 99), 1.64ug/L (20 Jan 99), 1.31ug/L (27 Jan 99), 1.38ug/L (3 Feb 99), 1.42ug/L (10 Feb 99), 1.53ug/L (17 Feb 99), 1.5ug/L (24 Feb 99), 1.5ug/L (3 Mar 99), 1.7ug/L (10 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (17 Mar 99), 1.6ug/L (24 Mar 99), 1.7ug/L (31 Mar 99), 1.4ug/L (7 Apr 99), 1.5ug/L (15 Apr 99), 1.5ug/L (22 Apr 99), 1.4ug/L (28 Apr 99), 1.7ug/L (12 May 99), 1.2ug/L (19 May 99), 1.3ug/L (26 May 99), 1.3ug/L (2 Jun 99), 1.3ug/L (9 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (16 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (23 Jun 99), 1.1ug/L (30 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (7 Jul 99), 1.2ug/L (14 Jul 99), 1.1ug/L (21 Jul 99), 1.2ug/L (28 Jul 99), 1.5ug/L (4 Aug 99), 1.4ug/L (11 Aug 99), 1.2ug/L (18 Aug 99), 1.2ug/L (25 Aug 99), 1.1ug/L (1 Sep 99), 1.2ug/L (8 Sep 99), 1ug/L (15 Sep 99), 0.9ug/L (13 Sep 99), 0.9ug/L (11 Nov 99), 0.7ug/L (16 Dec 99), 1ug/L (13 Jan 00), 1.2ug/L (17 Feb 00), 0.9ug/L (16 Mar 00), 0.7ug/L (13 Apr 00), 0.7ug/L (11 May 00), 0.7ug/L (15 Jun 00), Simazine: 2.66ug/L (30/7/98), 0.75ug/L (10 Sep 98), 0.5ug/L (23 Jun 99), 0.6ug/L (30 Jun 99).

Warren Reservoir poisoned with forestry herbicides Atrazine and Hexazinone 1998-2000.
Warren Reservoir Location 1
Atrazine: 2.48ug/L (20 Jul 98), 4.78ug/L (3 Aug 98), 7.91ug/L (3 Aug 98), 4.58ug/L (3 Aug 98), 5.22ug/L (3 Aug 98), 5.6ug/L (17 Aug 98), 5.69ug/L (7 Sep 98), 5.06ug/L (21 Sep 98), 3.74ug/L (19 Oct 98), 3.67ug/L (27 Oct 98), 3.25ug/L (4 Nov 98), 3.33ug/L (9 Dec 98), 3.05ug/L (16 Dec 98), 2.74ug/L (23 Dec 98), 2.93ug/L (6 Jan 99), 2.57ug/L (20 Jan 99), 2.4ug/L (3 Feb 99), 2.41ug/L (17 Feb 99), 2.3ug/L (3 Mar 99), 2.5ug/L (15 Mar 99), 2.3ug/L (7 Apr 99), 2.1ug/L (22 Apr 99), 2.2ug/L (28 Apr 99), 1.8ug/L (5 May 99), 1.9ug/L (12 May 99), 1.9ug/L (19 May 99), 1.7ug/L (25 May 99), 1.8ug/L (2 Jun 99), 1.6ug/L (9 Jun 99), 1.6ug/L (16 Jun 99), 1.5ug/L (23 Jun 99), 1.4ug/L (30 Jun 99), 1.5ug/L (7 Jul 99), 1.3ug/L (14 Jul 99), 1.3ug/L (21 Jul 99), 1.2ug/L (28 Jul 99), 1.3ug/L (4 Aug 99), 1ug/L (11 Aug 99), 0.8ug/L (18 Aug 99), 0.8ug/L (25 Aug 99), 0.8ug/L (1 Sep 99), 1.2ug/L (8 Sep 99), 0.5ug/L (6 Oct 99).
Hexazinone: 3.44ug/L (20 Jul 98), 4.85ug/L (3 Aug 98), 6.73ug/L (3 Aug 98), 3.65ug/L (3 Aug 98), 5.39ug/L (3 Aug 98), 5.17ug/L (17 Aug 98), 5.78ug/L (7 Sep 98), 5.79ug/L (21 Sep 98), 4.97ug/L (19 Oct 98), 5.11ug/L (27 Oct 98), 4.86ug/L (4 Nov 98), 4.35ug/L (18 Nov 98), 4.37ug/L (6 Jan 99), 4.22ug/L (20 Jan 99), 4.14ug/L (3 Feb 99), 3.89ug/L (17 Feb 99), 3.8ug/L (3 Mar 99), 3.7ug/L (15 Mar 99), 3.5ug/L (7 Apr 99), 2.8ug/L (22 Apr 99), 3.1ug/L (28 Apr 99), 3.2ug/L (5 May 99), 2.1ug/L (12 May 99), 2.6ug/L (19 May 99), 2.7ug/L (25 May 99), 2.3ug/L (2 Jun 99), 2.6ug/L (9 Jun 99), 2.8ug/L (16 Jun 99), 2.5ug/L (23 Jun 99), 2.5ug/L (30 Jun 99), 2.6ug/L (7 Jul 99), 2.4ug/L (14 Jul 99), 2.4ug/L (21 Jul 99), 2.3ug/L (28 Jul 99), 2.2ug/L (4 Aug 99), 1.7ug/L (11 Aug 99), 1.6ug/L (18 Aug 99), 1.8ug/L (25 Aug 99), 1.5ug/L (1 Sep 99), 1.6ug/L (8 Sep 99), 1.2ug/L (6 Oct 99), 0.7ug/L (3 Nov 99), 0.7ug/L (9 Dec 99), 0.8ug/L (6 Jan 00), 0.7ug/L (10 Jan 00), 0.6ug/L (9 Mar 00), 0.5ug/L (6 Apr 00),
Simazine: 3.93ug/L (3 Aug 98), 0.69ug/L (7 Sep 98), 0.7ug/L (23 Jun 99).
Warren Reservoir Location 2
Atrazine: 0.8ug/L (1 Jul 99), 0.7ug/L (9 Jul 99), Hexazinone: 15.7ug/L (1 Jul 99), 16.4ug/L (9 Jul 99), 4.4ug/L (18 Jul 99), 2ug/L (9 Aug 99), 2.2ug/L (5 Sep 99).
Warren Reservoir Location 4A
Hexazinone: 1.6ug/L (1 Jul 99), 0.8ug/L (9 Jul 99), 0.5ug/L (18 Jul 99)
Warren Reservoir Location 4B
Simazine: 3.1ug/L (6 Sep 99)
Warren Reservoir Location 5
Hexazinone: 3.7ug/L (1 Jul 99), 3.5ug/L (9 Jul 99), 1.2ug/L (18 Jul 99), 0.7ug/L (9 Aug 99), 0.6ug/L (5 Sep 99), 1.4ug/L (7 Oct 99), 0.6ug/L (14 Oct 99), 1.4ug/L (11 Nov 99), 1.2ug/L (3 Dec 99).
Warren Reservoir Location 6
Hexazinone: 5ug/L (1 Jul 99), 4.1ug/L (9 Jul 99), 2.3ug/L (18 Jul 99), 0.6ug/L (9 Aug 99), 0.8ug/L (5 Sep 99),
Warren Reservoir Location 11A
Atrazine: 0.5ug/L (9 Jul 99)
Hexazinone: 7.5ug/L (9 Jul 99), 5.9ug/L (9 Jul 99), 3.5ug/L (18 Jul 99), 2.9ug/L (9 Aug 99), 3.2ug/L (5 Sep 99)
Warren Reservoir Location 11B
Hexazinone: 1.4ug/L (1 Jul 99),
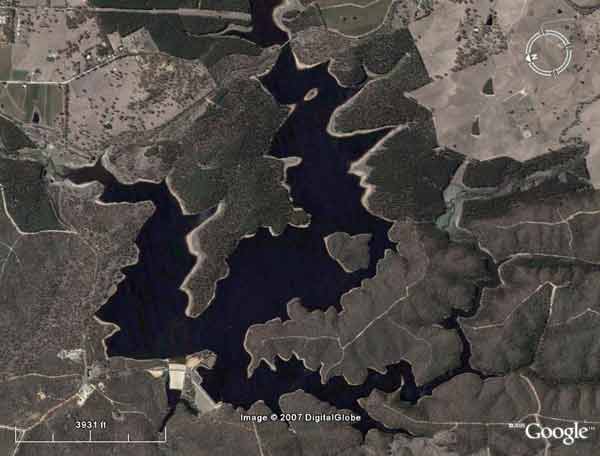

SA Water Plantations - South Para Reservoir - a source of Adelaide drinking water.
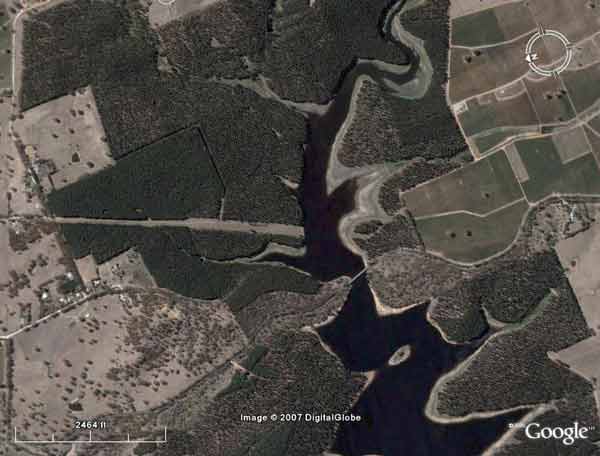

SA Water Plantations - South Para Reservoir - A source of Adelaide's drinking water

SA Water plantations. Adelaide drinking water - South Para Reservoir
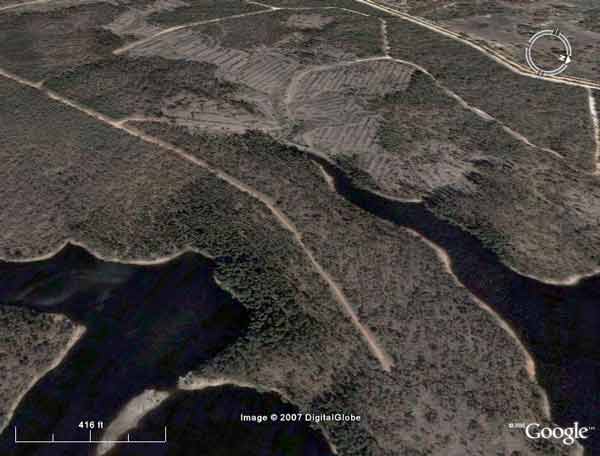

Adelaide drinking water - Logging in catchment of South Para Reservoir by Forestry South Australia. After the logging comes the herbicide application. What happens to the herbicides when it rains (heavily)?
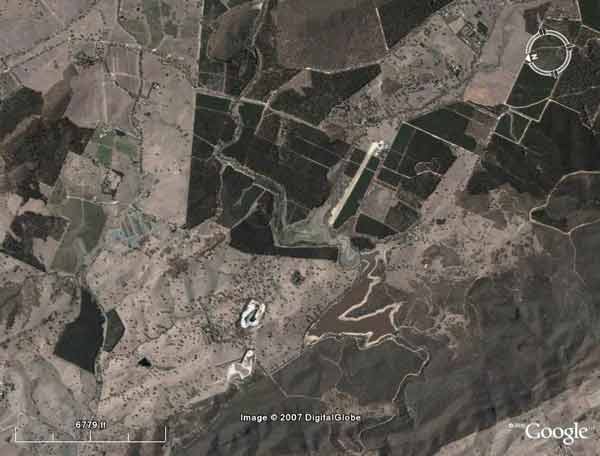

Forestry South Australia Plantations - Warren Reservoir - Adelaide drinking water
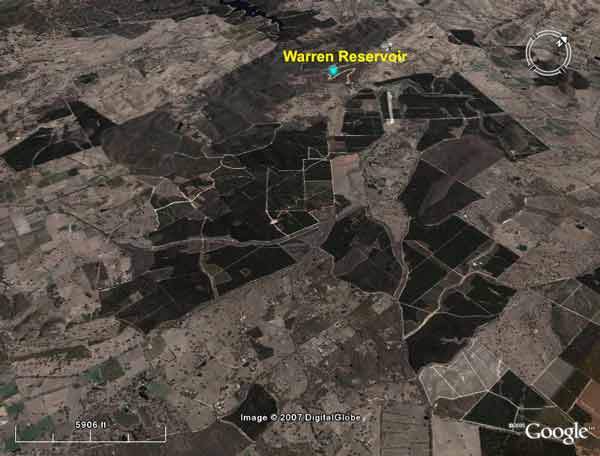
Forestry South Australia Plantations - Warren Reservoir - Adelaide drinking water. Over 3000 hectares of plantations lie upsteam of the Warren Reservoir.

October 2009: Myponga Reservoir. The reservoir supplies water to the southern metropolitan area and the south coast. Unlike other reservoirs Myponga does not receive any water from the River Murray but instead operates from water collected in the natural catchment.

October 2009: Recent logging of pine plantations surrounding Myponga Reservoir. What herbicides will be used for the next rotation?

Forestry South Australia Plantations - Millbrook Reservoir - Adelaide drinking water. Another 600 hectares of plantations upstream of a reservoir.

More plantations surrounding Mount Bold Resevoir in South Australia.

Kangaroo Island Bluegum plantation. The island has quite a large number of plantations.
"The company will close its Central Queensland pulpwood operation, after the report found the 2008 outbreak of Kirramyces fungal disease in part of the 25,650ha of pulpwood and solid wood ITC managed investment scheme plantations run by Elders Forestry had stripped it of value. The land, which included 29 freehold properties, would be cleared and put up for sale. Elders chief executive Malcolm Jackman said yields in Esperance were forecast to be lower than expected due to an average 50 per cent drop in rainfall in the region over the past five years, but he could not say how much they would fall by." Source: Elders To Write Down Forestry Assets (May 4 2010)
Hardwood Plantations Wiped Out by Fungal Disease (Kirramyces)
Source: Elders Forestry to Australian Stock Exchange
www.asx.com.au/asxpdf/20100503/pdf/31q45h1t5b94cv.pdf
Plantation Health & Protection Queensland Ė 41% of Project area
The central Queensland region comprises approximately 1,556 hectares across 5 properties, representing approximately 41% of the land area of the total Project.
The Project plantations were predominantly planted with the eucalypt hybrid E.grandis x E.camaldulensis (GxC) and Corymbia citriodora variegata (CCV). Clonal hybrids and seed stock were sourced from reputable suppliers and these species are commonly grown for commercial forestry in similar conditions as those found in central Queensland.
The Project plantations were established in 2007 and 2008.
In April 2006 EFM observed the first signs of leaf, bud and shoot blight disease in its central Queensland plantations, resulting in the defoliation of eucalypt trees and generally stunted growth of plantations. This was first identified as Halo Leaf Blight, but studies undertaken by plant pathologists subsequently concluded that a fungal pathogen belonging to the genus Kirramyces was the cause of the disease and studies were undertaken to assess the genetic susceptibility of the species used in the plantations.
To date, 14 species of the Kirramyces genus have been described by pathologists and probably many remain undescribed. Prior to this study, there had been limited investigation into the origin and movement of this group of pathogens and even today many aspects of this group need further research to be fully understood.
Phylogenetic and morphological studies revealed that the Kirramyces species associated with the fungal disease in central Queensland represented a new taxon described here as Kirramyces viscidus. Although the genus name is commonly used throughout this document, it refers to the species Kirramyces viscidus as indentified and described by plant pathologists.
Following identification of the Kirramyces disease, EFM surveyed the impact of the disease on affected Queensland plantations and undertook trials to assess options to remedy the impact of the disease such as the application of fertiliser and pesticides. In May 2007, results from clonal testing showed that the two primary commercial hybrid GxC clones used in the Queensland plantations, including the Project plantations, had a high susceptibility to the disease.
The incidence, spread and the impact of Kirramyces significantly increased during the summer of 2007/08, due to above-average rainfall promoting increased humidity which hastened the growth of the disease. Primarily due to these warm and humid conditions the impact of the disease considerably worsened and threatened the viability of the eucalypt plantations throughout central Queensland, including the Projectís plantations.
EFM and a range of independent authorities took all appropriate steps to identify, treat and prevent the disease from spreading, however no known combination of pesticides or any other silvicultural remedies could have prevented the Kirramyces disease from impacting the Project plantations in the way it has.
EFM has been working closely with the Queensland Department of Employment, Economic Development and Innovation, the CSIRO and other authorities since the disease was first noted. All agree that there is no known appropriate chemical or biological treatment to halt the spread of the disease or lessen the impact of Kirramyces on the Project plantations. In mid-2009 EFM undertook a detailed mapping and assessment to determine the extent of the disease damage to the Projectís properties.
The project area has been classified into three disease categories as at mid-2009 as follows:
|
Categorisation
|
Area (ha)
|
% of Queensland Project Area
|
|
Minor
|
128
|
8%
|
|
Moderate
|
420
|
27%
|
|
Severe
|
1,009
|
65%
|
The categorisation showed that the whole of the Projectís central Queensland plantations were impacted by Kirramyces with 92 per cent of the plantations being severely or moderately affected by the disease, and the remaining 8 per cent being affected to a lesser extent.
The forestry experts share the view that the Kirramyces disease will continue its spread through the plantations located in central Queensland, resulting in the certain negative recategorisation of the Project plantations.
Put another way, it is expected by forestry experts that the Projectís plantations will further deteriorate from minor to a moderate/severe categorisation.
The overall conclusion of the forestry experts is that the disease has killed or permanently and significantly stunted the growth of the plantation trees, such as to destroy any commercial value. This means that the central Queensland component of the Project will be discontinued in the immediate future. The Queensland plantations will then be cleared to prevent the uncontrolled spread of feral plants, pests and animals.
Replanting In accordance with the Product Disclosure Statement, the affected area will be replanted at EFMís cost. EFM has concluded that due to the Kirramyces disease, replanting of the destroyed area on properties located in central Queensland would not be in the best interests of Growers or the Project as a whole. As such EFM is in the process of sourcing suitable land available to lease to re-establish this part of the Project. Further information will be provided in due course.
Vast pine plantations on the Gnangara Mound north of Perth in Western Australia. Almost 10% of the Mound is covered with approximately 20,000 ha of pine plantations. The Gnangara Mound can supply Perth with between 40 & 60% of its drinking water. The pines use vast quantities of drinking water.

Brushy Rivulet Conversion, northern Tasmania, Meander River Catchment.
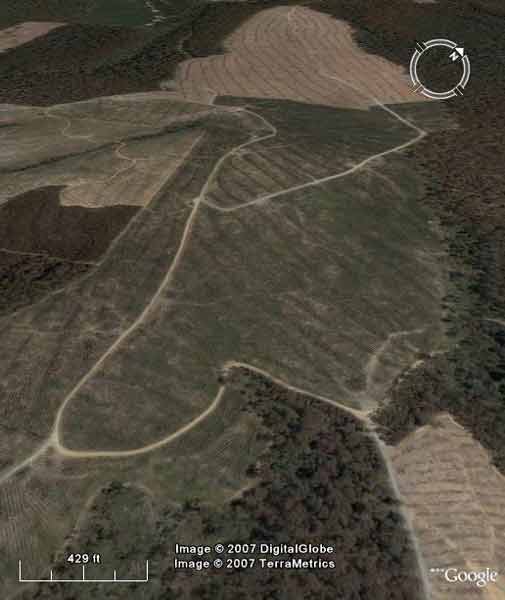
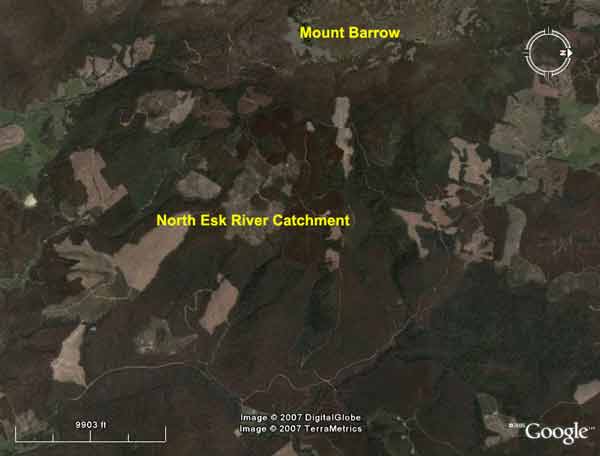
Tasmania - Burns Creek area, North Esk River Catchment, Launceston's Water Supply

Tasmania - Forester River Catchment, north of Branxholme.
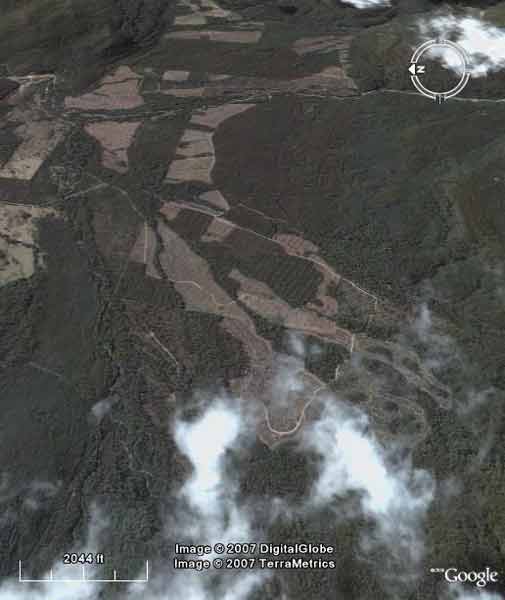

Tasmania - Meander River just downstream from headwaters.

Tasmania - Meander River Catchment south of Deloraine - Conversion of farmland to plantation.
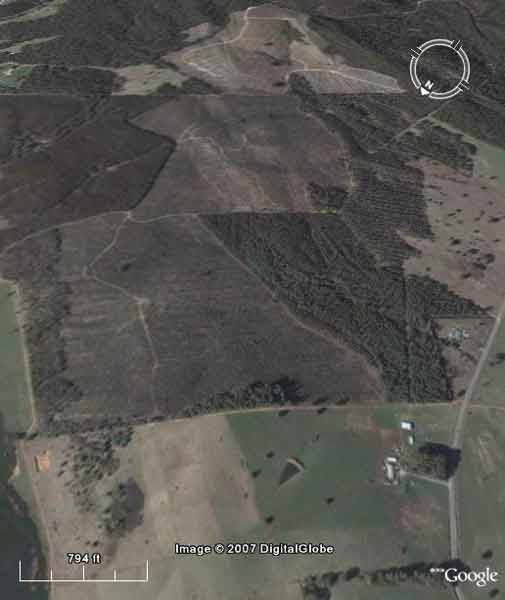
Tasmania - Meander River Catchment, south of Deloraine.

Tasmania - Wilmot River System (part of Forth River water supply)
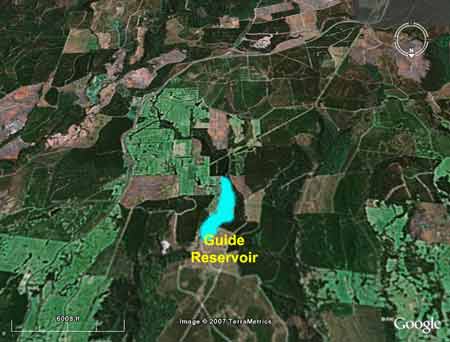
Guide Reservoir and surrounds in NW Tasmania. Guide Reservoir supplies drinking water to the city of Burnie as does the Cam River. In 2002 almost 27% of the Cam River catchment was covered in plantations.
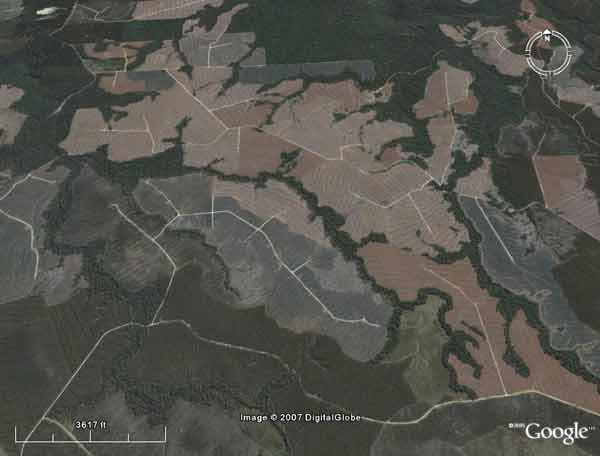
Wandle River in North West Tasmania. The Wandle River flows west into the Arthur River. Massive forest conversion to plantations has been occurring in this region.
Launceston Water Supply - Widespread conversion of native forests to plantations has occurred in Tasmania since the signing of the Regional Forest Agreements.





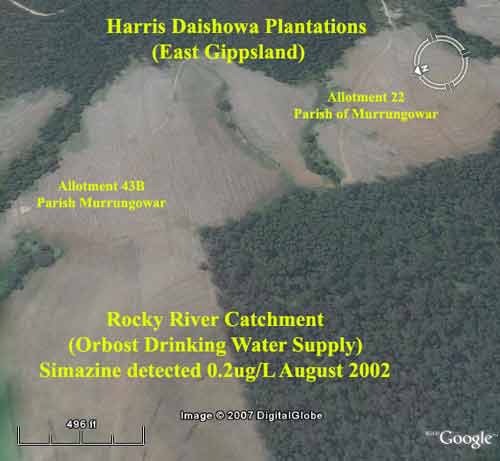
Simazine was detected by East Gippsland Water leaching from one of Harris Daishowa's plantations in the Rocky River catchment in August 2002. Rocky River provides the town of Orbost with drinking water.

Rocky River Plantations April 2010.

Rocky River Plantations April 2010.

Murrungower plantations - Orbost Water Supply.

Coolumbooka River: Bombala (Sth NSW) water supply has approximately 2000ha of plantations above its water supply offtake.

Bendoc in East Gippsland has ~300ha of Harris Daishowa plantations in its drinking water supply. Are nitens plantations at this location toxic?

Cabbage Tree Creek in East Gippsland also has ~150 ha plantations in its water supply catchment.

Bonang East Gippsland. Typical piston pump used to pump drinking water into isolated farm houses. Non treated water. The NSW town of Delegate which sources its drinking water from the Delegate River, has approximately 3000ha of plantations within its town water supply. Hundreds of other people are reliant on pumping water directly from streams, particularly in the Delegate River catchment.

State Forests NSW pine logging Little Plains River Catchment. People in Craigie also pump from local creeks. Thousands of hectares of pine plantations lie just over the Victorian/NSW border.

Queensborough River (East Gippsland) Shining Gum Plantations.

Queensborough River (East Gippsland) Shining Gum Plantations.

Jan 2008. Deep Creek, Foster's water supply. Great Southern Plantations 75ha of bluegum plantation to be established soon.

July 2007: Leongatha - South Gippsland Water Supply. Ruby Creek.

July 2007: Korumburra Water Supply - Bellview Creek Reservoir surrounded by pine plantations with new bluegums established on southern slopes of Bellview Creek.
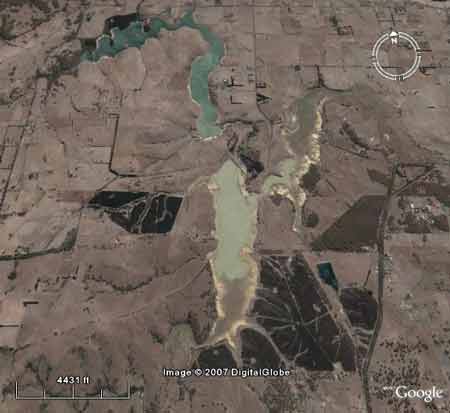
Upper Coliban Reservoir, with 200 hectares of bluegums established around the southern part of the reservoir (upstream of the reservoir) in the Coliban river catchment by East Victorian Plantation Forest Company of Australia Pty Ltd (Japanese Consortium). In a 'normal' rainfall year, after year 3, these plantations will use 400ML of water per year above that for the pasture that they replaced.

Strzelecki Ranges - October 2006: Recent pasture spraying most likely for establishment of bluegum plantations in Tarwin River East Branch - domestic water supply. Parish of Mirboo.

Swan Marsh: 2nd year herbicide application in bluegum plantation owned by Great Southern Plantations.

Forestry is another land use that can impact on water supply quality. This photo was taken in the Merino water supply catchment in western Victoria. This photo shows a pine plantation that has recently been logged. Herbicides are applied on pine plantations, post logging, to control competing native vegetation. At this site, it would be possible for herbicides to leach into groundwater which in turn is consumed by local residents.
Generally speaking, horticulture uses more pesticides than forestry, which in turn uses more pesticides than grazing. Therefore converting grazing country into forestry or horticultural areas will lead to an increase in pesticide use in those areas. But converting horticultural areas into forestry/plantation areas would lead to a significant decrease in pesticide use. However this rarely occurs due to the high value of horticultural land.

Jan 07: Penny Royal Creek catchment pine plantations and cropping in close vicinity to creek which is a proclaimed water supply for the residents of Geelong.

Jan 07: Pine plantations in close vicinity to the Gellibrand River (a domestic water supply for 50,000 people) in the Parish of Natte Murrang, 6km's north of Carlisle.

Jan 07: Timbercorp getting ready to spray bluegums in the vicinity of Swan Marsh, west of Colac. This was the site of a detailed VCAT case in January 2006 where locals residents didn't want bluegum plantations in their community. The community lost.